By WellnessMSN Team
Healthcare is entering a new era where treatments are designed specifically for you—not just people like you. This shift is called personalized medicine, and it’s changing the way we approach diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
🔬 What Is Personalized Medicine?
Personalized medicine (also known as precision medicine) is a medical approach that tailors treatments to the individual based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment. It moves away from the “one-size-fits-all” model to a more targeted, effective form of care.
For example, two patients with the same condition—say, breast cancer—may receive completely different treatment plans based on how their bodies react to certain therapies.
🧬 How Personalized Medicine Works
Here are the key tools and methods used:
1. Genetic Testing: Analyzes your DNA to identify health risks or drug responses.
2. Pharmacogenomics: Studies how your genes influence your response to medications.
3. Biomarker Identification: Biological markers help detect diseases early and choose effective treatments.
4. Digital Health Records + AI: Combining electronic health data with AI helps clinicians make data-driven decisions tailored to each patient.
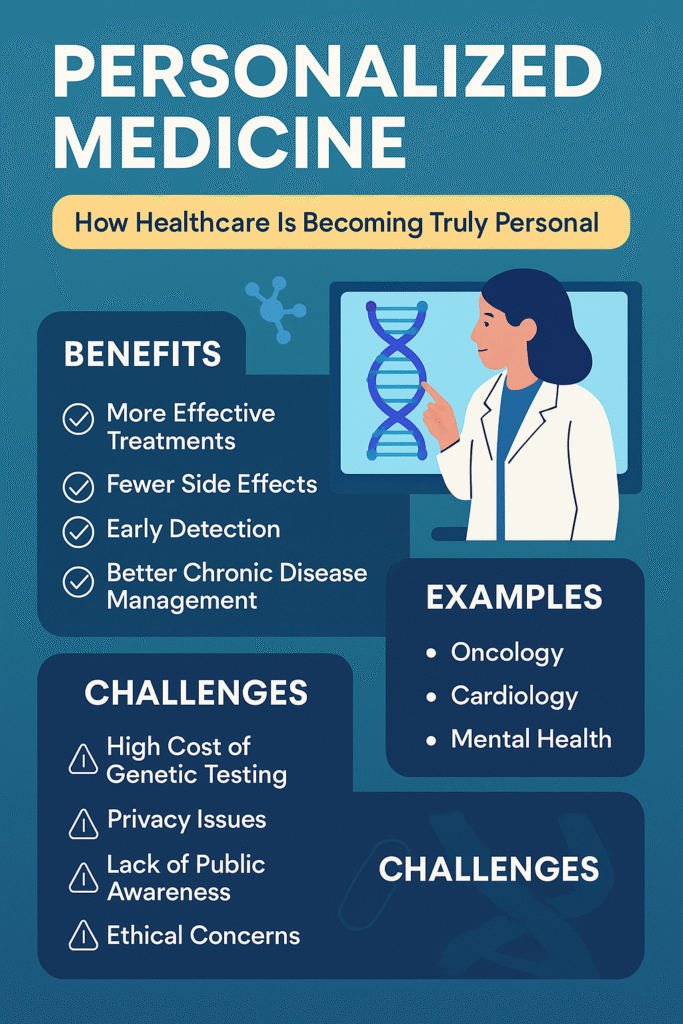
💡 Top Benefits of Personalized Medicine
- More Effective Treatments: Medications are chosen based on how your body responds—not trial and error.
- Fewer Side Effects: Targeted drugs reduce the risk of unnecessary reactions.
- Early Detection: Predictive testing can spot risks before symptoms appear.
- Better Chronic Disease Management: Custom care plans for conditions like diabetes or heart disease.
- Potential Long-Term Cost Savings: Avoids ineffective treatments and repeated hospital visits.
🏥 Real-World Examples of Personalized Medicine
- Oncology: Breast cancer treatments now often involve HER2 testing to guide therapy.
- Cardiology: Genetic tests help determine the right blood thinner dose.
- Mental Health: DNA testing may guide antidepressant selection.
- Diabetes: Personalized diet and treatment plans based on genetic factors.
⚠️ Challenges to Be Aware Of
- High Cost of Genetic Testing: Not all tests are affordable or covered by insurance.
- Privacy Issues: Handling genetic data responsibly is essential.
- Lack of Public Awareness: Many patients are unaware this care model exists.
- Ethical Concerns: Genetic information might raise questions about insurance or job discrimination.
🔮 The Future of Personalized Healthcare
The field is growing rapidly, powered by:
- AI and big data
- Home DNA testing kits
- Wearables that track real-time health metrics
- National and global genomic research initiatives
As these tools evolve, personalized medicine will become more mainstream—especially in managing chronic diseases, cancer, and preventive care.
🧠 What You Can Do
- Ask your healthcare provider if genetic testing is appropriate for you.
- Explore your family health history.
- Consider precision treatment options if you’re managing a chronic illness or planning preventive health steps.
